Cross Shard Transactions
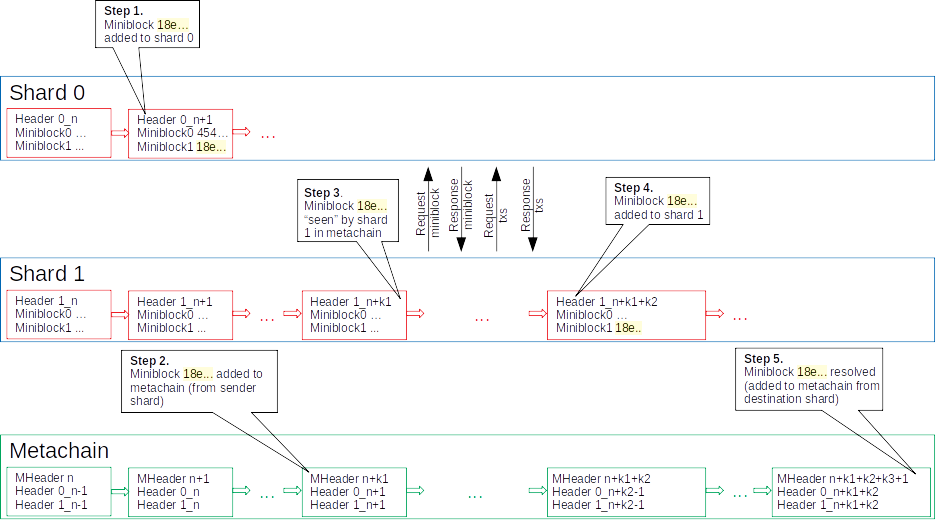
For an in depth example of how the cross-shard transactions are being executed and how the communication between shards and the metachain occurs, we are simplifying the entire process to just two shards and the metachain. Assuming that a user generates a transaction from his wallet, which has an address in shard 0 and wants to send EGLD to another user that has a wallet with an address in shard 1, the steps depicted in the figure below are required for processing the cross-shard transaction.
The block’s structure is represented by a block Header that contains information about the block (block nonce, round, proposer, validators timestamp etc.), and a list of miniblocks for each shard that contain the actual transactions inside. Every miniblock contains all transactions that have either the sender in the current shard and the receiver in another shard or the sender in a different shard and the destination in the current shard. In our case, for a block in shard 0, there will normally be 3 miniblocks:
- miniblock 0: containing the intrashard transactions for shard 0
- miniblock 1: containing cross-shard transactions with the sender in shard 0 and destination in shard 1
- miniblock 2: containing cross-shard transactions with sender in shard 1 and destination in shard 0. These transactions were already processed in the sender shard 1 and will be finalized after the processing in the current shard.
There is no limitation on the number of miniblocks with the same sender and receiver in one block. Meaning multiple miniblocks with the same sender and receiver can appear in the same block.
Processing
Currently, the atomic unit of processing in cross-shard execution is a miniblock: either all the transactions of the miniblock are processed at once or none and the miniblock’s execution will be retried in the next round.
Our cross-shard transaction strategy uses an asynchronous model. Validation and processing is done first in sender’s shard and then in receivers' shard. Transactions are first dispatched in the sender’s shard, as it can fully validate any transaction initiated from the account in this shard – mainly the current balance. Afterwards, in the receivers' shard, the nodes only need proof of execution offered by metachain, do signature verification and check for replay attack and finally update the balance for the receiver, adding the amount from the transaction.
Shard 0 processes both intra-shard transactions in miniblock 0 and a set of cross-shard transactions that have addresses from shard 1 as a receiver in miniblock 1. The block header and miniblocks are sent to the metachain. The metachain notarizes the block from shard 0, by creating a new metachain block (metablock) that contains the following information about each miniblock: sender shard ID, receiver shard ID, miniblock hash.
Shard 1 fetches the hash of miniblock 1 from metablock, requests the miniblock from shard 0, parses the transaction list, requests missing transactions (if any), executes the same miniblock 1 in shard 1 and sends to the metachain resulting block. After notarization the cross transaction set can be considered finalized.
The next diagram shows the number of rounds required for a transaction to be finalized. The rounds are considered between the first inclusion in a miniblock until the last miniblock is notarised.